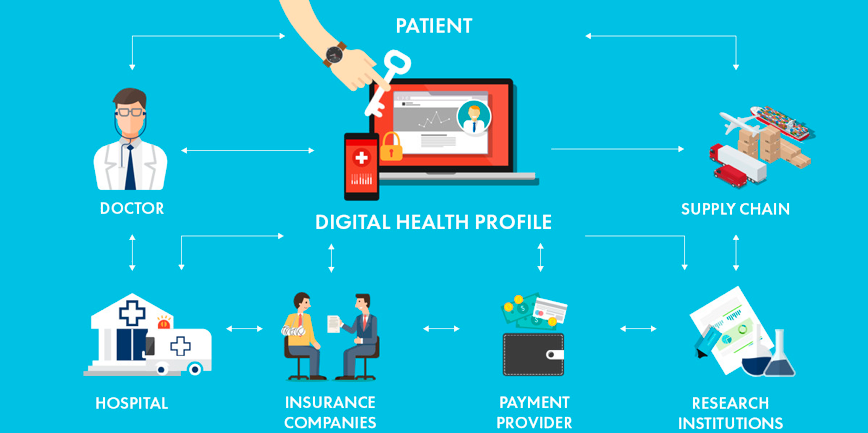
Blockchain technology, a decentralized digital ledger system, has gained significant attention in various industries due to its security, transparency, and immutability. One sector that is exploring the potential of blockchain is healthcare. In this blog, we will delve into the intersection of blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies, and healthcare systems.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain is a distributed digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers so that any involved record cannot be altered retroactively without the alteration of all subsequent blocks and the consensus of the network. It was invented in 2008 for the digital currency bitcoin as a core component of its design, but it has since been used for other applications. The decentralized nature of blockchain makes it an attractive solution for industries seeking secure data transfer and storage.
Cryptocurrencies in Healthcare
Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual currencies secured by cryptography for security. Bitcoin, the first decentralized cryptocurrency, was created using blockchain technology. In healthcare, cryptocurrencies can be used for various applications such as:
Payment Processing: Cryptocurrencies offer faster and cheaper transactions compared to traditional payment methods like credit cards or bank transfers. This can be particularly useful in healthcare where timely payments are crucial.
Patient Data Monetization: Patients can monetize their health data by selling it to researchers or insurers through a secure blockchain platform. Smart contracts can ensure that patients receive fair compensation while maintaining their privacy.
Fraud Detection: Blockchain’s transparency and immutability make it an effective tool for detecting fraudulent activities in healthcare claims processing or prescription drug supply chains.
Medical Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can help ensure the authenticity and quality of medical supplies by creating an immutable record of their origin and journey from manufacturer to end user. This is crucial in preventing counterfeit drugs from entering the market.
Clinical Trials: Blockchain can facilitate clinical trials by securely storing patient data and ensuring data integrity while maintaining patient privacy using encryption techniques like zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs). This can help reduce trial costs and increase efficiency by eliminating intermediaries like Clinical Research Organizations (CROs) or Contract Research Organizations (CROs).
Telehealth Services: Blockchain can enable secure payment processing and data sharing between patients and healthcare providers during telehealth consultations using smart contracts on decentralized platforms like Ethereum or EOS (EOS link: https://eosauthority.com/). This ensures that sensitive patient information remains private while allowing seamless transactions to occur on a trusted network.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Applications: DeFi applications built on blockchains like Ethereum (Ethereum link: https://ethereum.org/) allow users to lend, borrow, trade assets directly with one another without intermediaries like banks or financial institutions – this could potentially disrupt traditional financing models within healthcare industries such as insurance companies or venture capital firms who currently act as gatekeepers for funding research or development projects (Web3 Foundation link: https://web3.foundation/).
Personal Health Records: Patients can maintain their own personal health records on a decentralized blockchain platform using applications like MedRec (MedRec link: https://github.com/medrec/medrec). These records are encrypted and controlled by the individual patient themselves, providing them with greater autonomy over their data while ensuring its security through cryptographic algorithms such as elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) or SHA-256 hashing algorithms commonly used in blockchains like Bitcoin or Ethereum. 9. Supply Chain Financing: Blockchain-based supply chain financing solutions like VeChainThor (VeChainThor link: https://www.vechain Thor .com/) provide real-time tracking of inventory movements along with financing services for businesses involved in complex global supply chains – this could potentially improve cash flow management within healthcare systems. 10. Pharmaceutical Industry Regulation: Blockchain technology can be used to create tamper-evident records that track every stage of drug production from raw materials to final packaging – helping ensure regulatory compliance within pharmaceutical industries.